
A Guide to Anti-Money Laundering for Digital Banks
Based on expert advice and interviews with sector leaders, our comprehensive guide takes you through every step in the compliance process for digital banks.
Download your copyAs banks and other financial institutions (FIs) embrace advances in financial technology, the digital banking sector has grown dramatically. This trend shows no signs of slowing down: one survey suggests 86 percent of UK adults use some form of online or remote banking in 2024, while 36 percent have a digital-only bank account, compared with 24 percent in 2023.
However, as digital banking services become more sophisticated, so do the criminal methodologies designed to target them. To combat these, firms must be aware of their regulatory obligations, with the banking sector suffering the second-heaviest fines for breaches in 2023. They must then prioritize developing robust anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) measures to ensure their appeal to consumers does not come at the cost of compliance.
Most countries worldwide have developed specific and comprehensive AML/CFT regulatory frameworks, which apply equally to digital banks, traditional FIs, and certain non-financial sectors such as casinos, high-value dealers, and real estate firms.
As digital banking grows, these institutions face the same regulatory obligations as their traditional counterparts. However, due to the high costs and complexity of obtaining a banking license, many digital banks opt to partner with fully licensed, established banks. While such partnerships may help digital banks navigate certain regulatory requirements, they remain fully responsible for their own compliance with AML laws. Relying solely on their partners’ compliance measures is insufficient to mitigate their legal responsibilities or risks.
Therefore, all digital banks must be aware of the specific AML/CFT laws in each jurisdiction in which they operate, as well as the regulatory bodies responsible for enforcement. The following outlines key legislation and regulators in major jurisdictions:
Most jurisdictional AML regulations take their cue from the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) International Standards on Combating Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism & Proliferation, or ‘40 Recommendations’. These set the standard for international AML and center around a core set of principles:
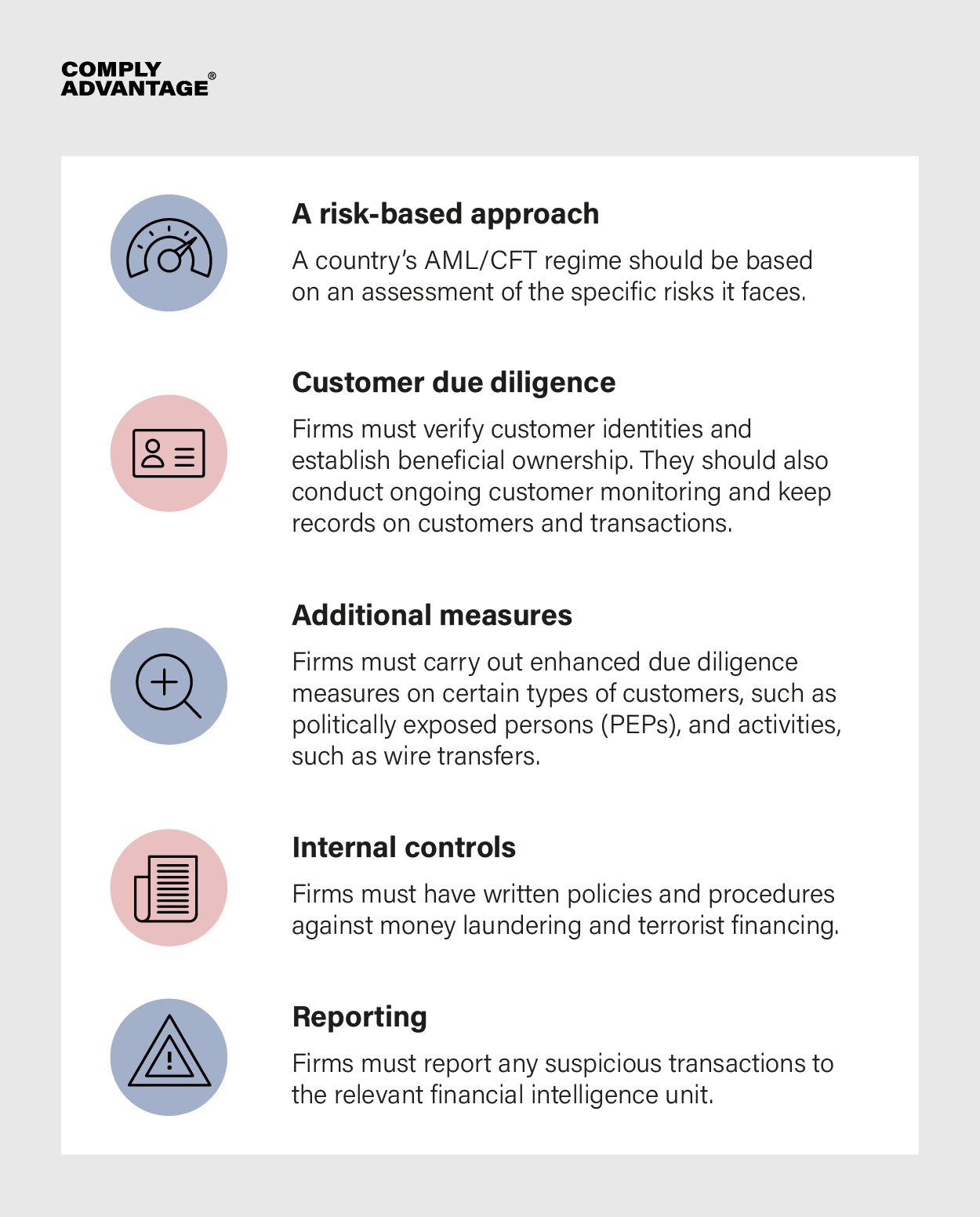
To develop a risk-based approach, firms should conduct initial (and frequently updated) risk assessments to determine the kinds of risk they are most likely to face, laying the ground for their AML policies.
Ongoing customer monitoring is one key internal control firms should adopt; per EU regulations introduced in 2024 requiring payment service providers (PSPs) to be able to send and receive instant payments, FIs must be able to conduct at least daily customer screening. Another is transaction monitoring, which enables firms to detect and flag any unusual transactions or suspicious patterns that develop. When this happens, FIs should report it using a suspicious activity report (SAR).
As technology-focused businesses, digital banks should be fully capable of developing electronic know your customer (KYC) and customer due diligence (CDD) processes, though they should ensure their processes align with the FATF’s published guidance for FIs using digital ID.
Digital banks face both conventional money laundering risks and those that have emerged from advances in financial technology. However, although they may encounter the same financial crime typologies and regulations as other kinds of banks and FIs, this does not mean they share the exact same set of compliance challenges. For digital banks, these challenges are often caused by:

Based on expert advice and interviews with sector leaders, our comprehensive guide takes you through every step in the compliance process for digital banks.
Download your copyTo manage AML risks, digital banking service providers must take clearly defined approaches to regulatory compliance. In practice, this means firms should optimize their processes for collecting and analyzing customer data in a digital landscape. Effective components of an AML compliance program for digital banks include:
Implementing advanced AML software should be a natural step for innovative FIs such as digital banks. However, with multiple options available to them, firms should consider their specific needs and which of the advantages this technology can provide will serve them best. Specific factors to look out for include:
Fortify your organization and fuel your growth with dynamic solutions tailored to your needs. Book your free demo today and find out why 1000s already use ComplyAdvantage.
Get a demoOriginally published 09 July 2020, updated 17 October 2024
Disclaimer: This is for general information only. The information presented does not constitute legal advice. ComplyAdvantage accepts no responsibility for any information contained herein and disclaims and excludes any liability in respect of the contents or for action taken based on this information.
Copyright © 2025 IVXS UK Limited (trading as ComplyAdvantage).