In February 2024, the European Parliament issued new regulations to ensure financial transactions reach their recipients instantly across the European Union. The new rules update certain regulatory requirements for banks and other types of payment service providers (PSPs). In addition to this, the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) Instant Credit Transfer (ICT) rulebook was amended.
In light of these developments, this article will shed light on the evolving EU payments landscape by exploring:
- What is SEPA, what are the benefits it offers, and what are the countries within the SEPA zone?
- The SEPA legal framework and the regulations that support it.
- How SEPA is connected to the EU’s instant payments regulatory reform.
What is SEPA?
SEPA is a framework established by the EU that harmonizes euro-denominated payments across participating countries. The framework’s main objective is to create a more efficient market for payments across Europe by allowing for seamless euro transactions, eliminating the distinctions between domestic and cross-border payments.
How do SEPA payments work?
SEPA payments are any euro-denominated payments made between accounts in the SEPA zone using standardized procedures and formats, including:
- Credit transfers.
- Direct debits.
- ATM withdrawals.
- Payments by debit and credit cards.
- Money remittance.
What is a SEPA mandate?
A SEPA mandate is a foundational element of SEPA payments, serving as the payer’s permission for their bank account to be debited. Initially, SEPA mandates had to be signed on paper. However, in 2012, the European Council wanted to harmonize payment systems in euros. As a result, Regulation (EU) 260/2012 was passed into law, which promoted the transition to digital mandates.
The electronic mandate is essentially evidence for billers to justify debits and protect against any claims that unauthorized transactions have taken place. If such transactions do occur, payers can request refunds within 13 months.
The benefits of using SEPA payments
SEPA payments offer financial institutions numerous advantages, including:
- SEPA payments typically involve lower fees than traditional cross-border payments, resulting in greater cost efficiency.
- Transactions within the SEPA network are processed quickly, often within one business day, ensuring timely payments and efficient cash flow management.
- SEPA enhances convenience and simplifies payments by standardizing procedures across all participating countries.
- SEPA payments come with clear pricing and fewer hidden costs, making it easier for users to understand the fees involved.
- Enhanced security measures and robust regulatory protections are integral to SEPA payments, ensuring transactions are secure and mitigating the risk of fraud.
- SEPA establishes uniform payment formats and procedures. This standardization facilitates smoother and more efficient transactions, reducing errors and processing times.
- SEPA covers all 27 EU member states and several non-EU countries, making it easier for businesses to expand their operations across Europe.
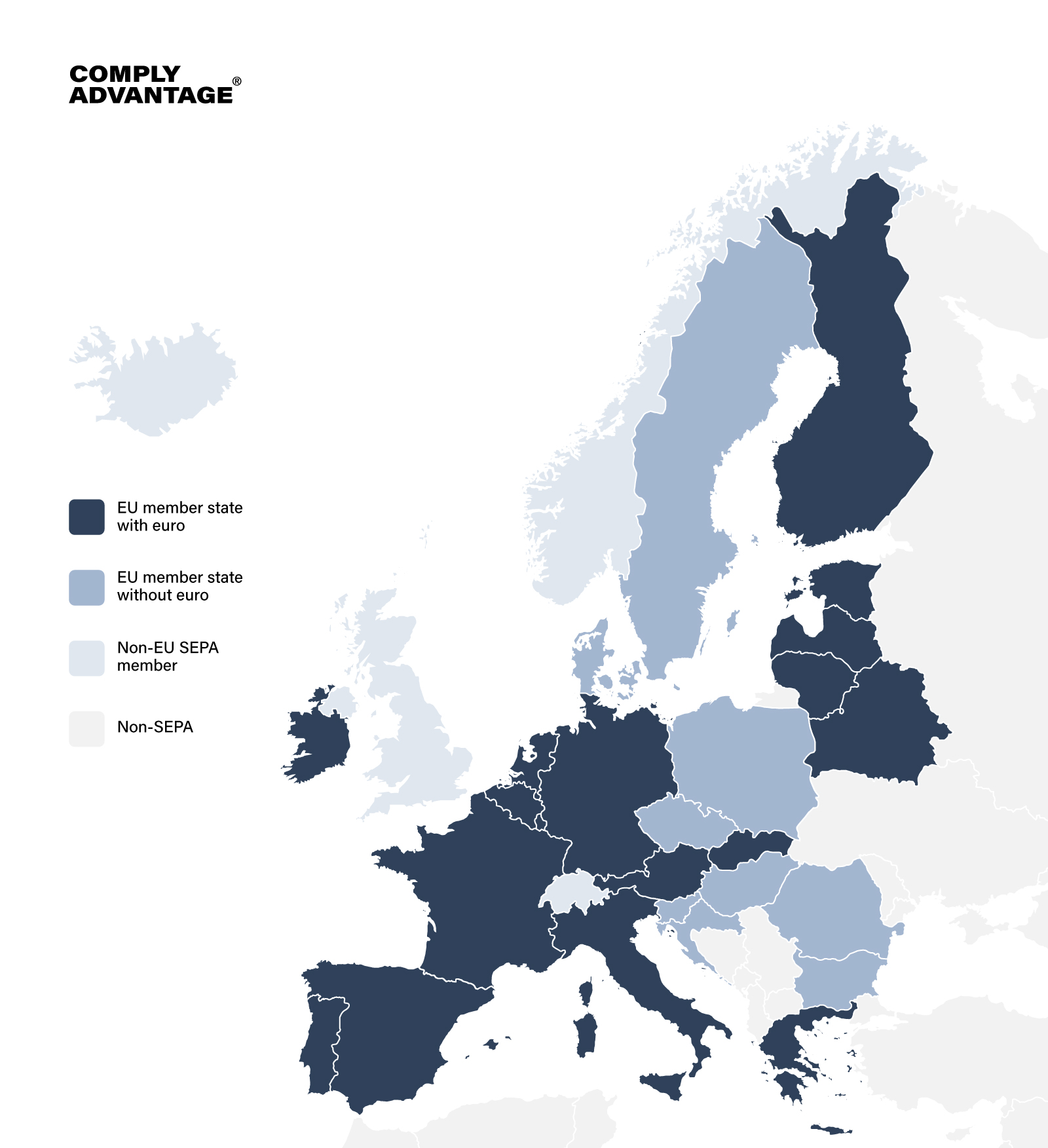
What are the SEPA countries?
The SEPA zone encompasses 36 countries, including EU member states and additional countries that have opted to participate in the initiative. The countries in SEPA are:
| Andorra
Austria Belgium Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Latvia |
Liechtenstein
Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Monaco Netherlands Norway Poland Portugal Romania San Marino Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland United Kingdom Vatican City |
SEPA legal framework and regulations
A robust legal framework underpins the SEPA initiative to ensure smooth operations and compliance across all member states. The foundation of SEPA lies in several key regulations and directives:
- Regulation (EU) No 260/2012 sets the technical and business requirements for credit transfers and direct debits in euros.
- Payment Services Directive (PSD2) enhances consumer protection, promotes innovation, and improves the security of payment services.
- E-money Directive (EMD2) governs the issuance of electronic money and the establishment of e-money institutions, ensuring they operate under a harmonized regulatory framework.
What are the five SEPA payment processing schemes?
Building on this legal foundation, the European Payments Council (EPC) developed five distinct SEPA payment processing schemes, each designed to cater to different types of transactions.
- The SEPA Credit Transfer (SCT) scheme enables the transfer of funds in euros between accounts in the SEPA zone – ideal for one-off payments such as salary payments, supplier invoices, or any general payment where a paper-based process can be eliminated.
- The SEPA ICT scheme provides for near-instant euro transfers between accounts within the SEPA zone – suitable for urgent or time-sensitive transactions, such as emergency funds transfers or real-time payment needs.
- The SEPA Direct Debit Core (SDD Core) scheme allows payees to collect funds from a payer’s account, given that the payer has granted prior authorization – commonly used for recurring payments such as utility bills or subscriptions.
- The SEPA Direct Debit Business-to-Business (SDD B2B) scheme is similar to the Core scheme but requires both the payer and the payee to be registered as businesses and offers a shorter refund period.
- The one-leg out instant credit transfer (OCT Inst) scheme is designed to facilitate instant credit transfers where one participating financial institution is outside SEPA. This scheme enables cross-border payments to or from non-SEPA countries, ensuring fast and efficient transactions.
EU instant payments regulatory reform
Despite three of these five schemes focusing on instant payments, the market remains fragmented. In fact, in 2023, only about one in ten euro credit transfers in the European Union were processed as instant payments.
To promote real-time payments in Europe, the European Council has prioritized establishing a fully integrated instant payments market. As mentioned previously, a new regulation (Regulation (EU) 2024/886) was introduced in early 2024 to achieve this, amending the SEPA ICT rulebook and setting out the following requirements for firms:
- PSPs must offer instant payments – completed within 10 seconds – through the same channels used for initiating other credit transfers.
- The payer’s PSP must verify the payee’s details before clearing payments. If discrepancies are found, the payer must be notified and given the choice to cancel the transaction or proceed despite the discrepancies.
- Firms must screen payees against sanctions lists whenever new announcements or updates to existing sanctions are made. These screenings must occur before payment authorization and should not interrupt the execution of instant payments.
- Firms are obligated to report specific details related to the charges associated with credit transfers, ICTs, and payment account activities.
- Firms must disclose the volume of national and cross-border transactions that were rejected due to sanctions screening.

A Guide to Financial Crime and SEPA Instant Payments
The drive for innovation is changing the payments landscape in Europe. This report is an essential guide for European compliance officers operating in the SEPA region.
Download nowChallenges of new instant payments regulations in Europe
The introduction of new instant payment regulations in Europe presents several compliance challenges for FIs across the SEPA zone. These include:
1. Upgrading payment infrastructures
By January 9, 2025, all PSPs in the EU must be able to receive instant payments. By October 9, 2025, PSPs must also offer the facility to send instant payments at an affordable rate. Many firms may find their current payment infrastructures need significant upgrades to keep pace with these deadlines.
2. Integrating financial crime controls
Integrating refined financial crime controls may be challenging as firms transition to SEPA ICT. Compliance processes – such as know your customer (KYC), name screening, payment screening, and fraud detection – each involve distinct applications that must be integrated to ensure effective compliance. The primary challenge here lies in synchronizing these various applications within the incredibly fast-paced environment of instant payments. Each process needs to function efficiently with the others to avoid delays that could negatively impact the speed of transactions.
3. Enhancing sanctions screening
Under the new regulations, banks and PSPs must verify whether their users are subject to targeted financial restrictive measures (on a daily basis at minimum). The challenge here lies in balancing the need for thorough sanctions screening with the demands of processing payments quickly.
How to comply with the EU’s evolving instant payments regulations
As the EU continues to update its regulations to standardize cross-border instant payments, firms will be faced with new requirements under a tiered implementation schedule. Some top tips for firms to ensure compliance include:
- Continue to enhance existing AML/CFT practices by updating risk assessment protocols, employee training programs, and transaction monitoring systems to detect and report suspicious activities promptly.
- Verify payee information thoroughly before payment authorization, including cross-referencing payee details with official identification documents and maintaining records of verification processes.
- Regularly update sanctions screening processes to reflect the latest EU and international sanctions lists. Screen payment service users (PSUs) against these lists upon any updates rather than during payment execution to avoid delays and ensure compliance.
- Set up robust monitoring and reporting systems capable of generating detailed compliance reports. These systems should track all transactions, flag anomalies, and ensure the timely submission of mandatory reports to regulatory bodies in accordance with EU standards.
- Utilize advanced technology solutions to efficiently manage compliance, scalability, and screening processes.
Improve your organization’s operational efficiency
1000s of organizations are already using ComplyAdvantage. Learn how to streamline compliance and mitigate risk with industry-leading solutions.
Get a demoOriginally published 17 September 2024, updated 11 February 2025
Disclaimer: This is for general information only. The information presented does not constitute legal advice. ComplyAdvantage accepts no responsibility for any information contained herein and disclaims and excludes any liability in respect of the contents or for action taken based on this information.
Copyright © 2026 IVXS UK Limited (trading as ComplyAdvantage).